Scientists Publish on Stink Bug's Favorite Plants, Damage
 |
 |
|
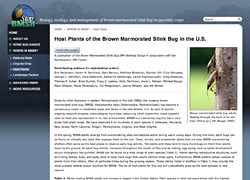
BMSB uses 170 plants for food and reproduction. View the list at StopBMBS.org. |
Videos show how to monitor for damage and infestations. Watch them at StopBMSB.org. |
Researchers have published a list of 170 plants that the brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) uses for food and reproduction, called Host Plants of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug in the U.S. “This publication will be a living document, updated regularly on the web,” said North Carolina State University researcher Jim Walgenbach, one of the scientists who contributed to the project.
The list is a companion to five short web videos about BMSB host plants that show growers how to monitor for damage and infestations. Topics span orchard crops, small fruit, vegetables, ornamental crops, and Pacific Northwest host plants and damage. The segments, which can also be watched as one 20-minute video, are the latest installment in the “Tracking the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug” series produced by the Northeastern Integrated Pest Management Center at Cornell University. Earlier videos explain history and identification, overwintering and spread, and monitoring and mapping.
BMSB has been detected in 40 states, posing severe agricultural problems in six states and nuisance problems in thirteen others. The insect threatens an estimated $21 billion worth of crops in the United States alone.
— by CHRIS GONZALES
StopBMSB.org provides information about our team's efforts to control brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB), through funds provided by the USDA's Specialty Crop Research Initiative. If republishing our news, please acknowledge the source ("From StopBMSB.org") along with a link to our website.
